Nonferrous metal, Metallic powders, Metal Compounds,Metal products from www.metal-powder-dust.com
Thursday, April 12, 2012
What is Cerium (III) iodide?
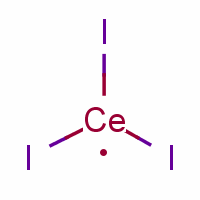
Cerium (III) iodide
CAS Number: 7790-87-6
Molecular Weight: 520.83
Molecular Formula: CeI3
Physical Appearance: powder
Melting point: 761 ° C
Boiling point: 1397 ° C
Solubility:-205kJ/mol at 20 ° C water
Description of Cerium (III) iodide
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet Ceres (itself named for the Roman goddess of agriculture). Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight. It is found in a number of minerals, the most important being monazite and bastnasite.
Cerium(IV) (ceric) salts are orange red or yellowish, whereas cerium(III) (cerous) salts are usually white or colorless. Both oxidation states absorb ultraviolet light strongly. Cerium(III) can be used to make glasses that are colorless, yet absorb ultraviolet light almost completely. Cerium can be readily detected in rare earth mixtures by a very sensitive qualitative test: addition of ammonia and hydrogen peroxide to an aqueous solution of lanthanides produces a characteristic dark brown color if cerium is present.
More about: Cerium (III) iodide sale
Read more: Metal Compounds
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment